
Typically, muons last only 2.2 microseconds before they decay. Muons are unstable and will spontaneously decay into other particles. The muon (µ –) is essentially identical to an electron except that it is 207 times more massive. The electron is stable, meaning it will never spontaneously change into any other particle. It is thought to be the least-massive charged particle. 6 Of these, the electron (represented by the symbol e – or β –) is the lightest, with a mass of only 9.109 × 10 -31 kilograms. Three of the six leptons-the electron, the muon, and the tau (or tauon)-have an electrical charge of negative one (-1). (Physicists had not yet discovered the heaviest lepton, the tau, when they coined the name.) There are six types (called flavors) of leptons, and five of the six are indeed very low-mass. Lepton comes from a Greek word and basically means small or thin-a reference to the extremely low mass of the electron relative to protons and neutrons. The electron is one of the 18 known types of elementary particles and is a member of a class of particles called leptons. The nucleus of the hydrogen atom-a single proton-is more than 10,000 times smaller! The implication is hard to imagine but quite clear: Atoms are mostly empty space.Įlectrons are thought to be elementary (or fundamental)-meaning they are not made up of other particles. Its diameter is roughly 1.06 × 10 -10 meters that is one ten-millionth of a millimeter. The nucleus of an atom is unimaginably small, even when compared to the size of an atom. This is because protons and neutrons are each over 1,800 times more massive than an electron. 5Īlmost all the mass of an atom is contained in its nucleus. Generally, the number of electrons in the orbitals of an atom exactly matches the number of protons in the nucleus, resulting in an electrically neutral atom. Otherwise, a peak would “cancel out” a trough there would be no wave left and hence no electron (Figure 2).
An electron can only orbit at distances where the peaks and troughs of its wave self-align. Rather, they sometimes act as if they were “spread out” much like the wave that forms when a rock is dropped in a lake. Physicists have discovered that subatomic particles do not always behave as if they were at one specific location in space. The reason orbitals are quantized has to do with the wave nature of electrons. This is where we get the term quantum physics. In physics, when only certain values are allowed (i.e., physically possible), like the orbitals of an atom, the system is said to be quantized. These special distances are called orbitals. But electrons can only orbit at certain specified distances from the nucleus. Second, given the right speed, a planet can orbit at virtually any distance from the sun. But there are some differences.įirst, planets orbit the sun because of the force of gravity, whereas electrons orbit due to the force of electromagnetism. Since opposite electrical charges attract, electrons orbit the nucleus, much as planets orbit the sun. The number of protons determines the type of atom. The nucleus is made of positively charged protons and neutral neutrons. An atom consists of a central positively charged nucleus surrounded by one or more electrons, which have a negative electrical charge (Figure 1). But atoms are composite particles, meaning they are made of even smaller particles. In school, students are taught that atoms are the basic building blocks of matter, comprising everything we can touch. We begin our journey with something familiar: the atom.
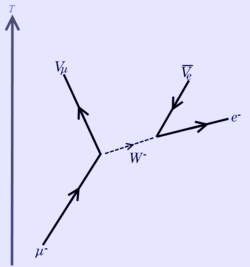
Unstable lepton muon series#
In this series of four articles, we will examine the various families of subatomic particles, their interesting behaviors, how they are classified, and how they often confound secular thinking. Just as a cat is a mammal, a vertebrate, and an animal, so a proton is a baryon, a hadron, and a fermion.

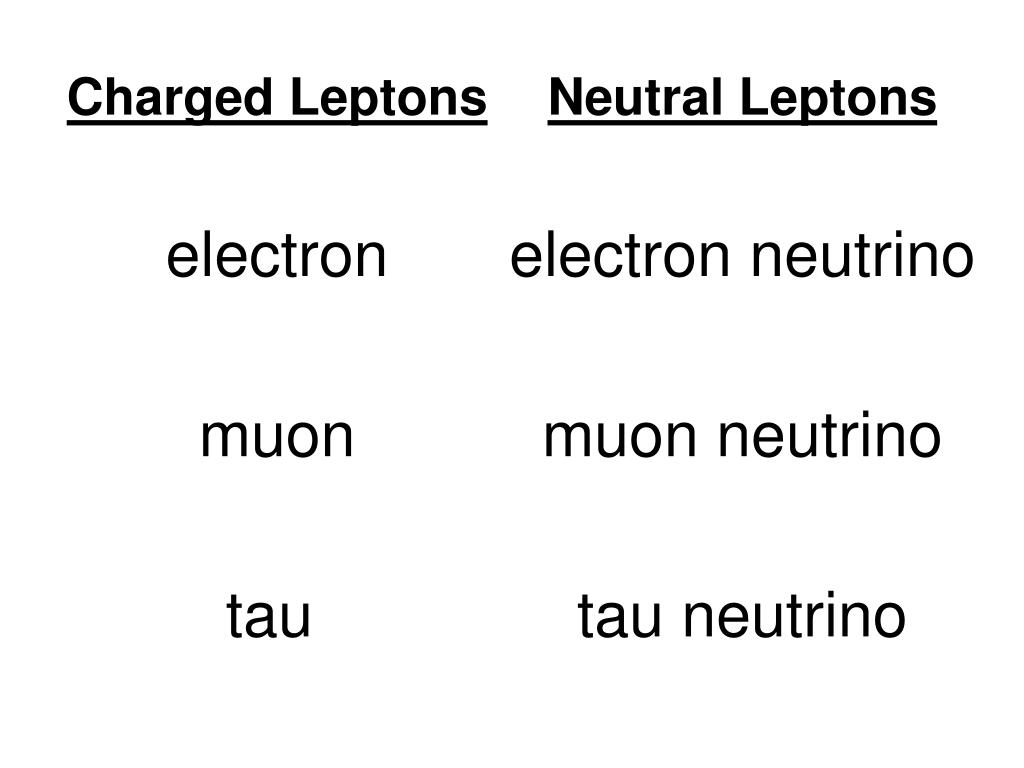
1,2 Since God is a rational Being and has imposed order on creation, 3 physicists can classify particles by their properties in a hierarchy much the same way biologists classify living organisms. Neutrinos are merely one of the several dozen subatomic particles that exist in nature. How is this possible? And why are neutrinos able to pass through solid matter? Their ability to pass through solid matter makes neutrinos very difficult to detect, yet we know they exist. These ghostly particles are produced in the core of the sun and other stars, where they stream away at nearly the speed of light. *Īs you read this sentence, trillions of invisible particles called neutrinos are streaming harmlessly through your body.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
